Boost Vs Buck Converter Efficiency
For a buck converter by varying the duty cycle of the switch a desired average voltage output can be achieved. There are two types of topologies viz.

Buck Boost Vs Buck Converter It S About Battery Life In Portables Ee Times
The fundamental reason has to do with the inductor current flowing directly to ground during the on-time instead of through the load like it does on Buck converters.

Boost vs buck converter efficiency. Efficiency of synchronous versus nonsynchronous buck converters Choosing the right DCDC converter for an application can be a daunting challenge. In conclusion a performance comparison of a buck versus a boost converter shows the inherent superiority of the buck converter in BOM cost PCB size efficiency accuracy and EMI. Voltage correction with buck-boost transformers are small such as 240V to 208V 220V to 240V 450V to 480V 120V to 110V and etc.
But for some reason as I increase this duty cycle with my input voltage kept constant the power efficiency of the converter goes down. The buckboost converter is a type of DC-to-DC converter that has an output voltage magnitude that is either greater than or less than the input voltage magnitude. This engineering essentials on buck converter efficiency presents the relevant equations needed to estimate power losses in the converter.
That is true for a Buck input cap. A buck topology or buck converter is one of the most used basic topology used in SMPS. For a Buck-Boost the input cap RMS increases dramatically and steadily for all duty cycles from 0 to 1.
Buck converters and LDOs have their own upsides and downsides. Less than 50then the buck converter is used. Boost converters are typically less efficient than Buck converters but not by much.
For a battery voltage greater than 36V the buck-boost operates as a buck converter while for an input voltage less than 36V it behaves similar to a buck-boost or boost converter. Both buck boost converters are DC to DC converters with different voltage and current at the output compare to input. Fig 2- Circuit schematic of a buck converter.
To further improve their efficiency it is helpful to understand the basic mechanism of power loss. Buck Converter Background. Inverting and non inverting.
Eventhough buck boost converter is cheaper than cuk converter limitations such as discontinuous input current high peak current in power components poor transient response etc of buck-boost. Typical power-supply issues are size efficiency cost temperature accuracy and transient. The term buck refers to stepping down voltages while boost refers to stepping up voltages.
A typical synchronous buck circuit using MOSFETs as a switch is shown in. It is equivalent to a flyback converter using a single inductor instead of a transformer. The devices can also be applied to handle low voltage distribution 12V 24V 32V or 48V.
Also in case of boost regulator the output voltage is higher than the input voltage but in buck regulator the output voltage is lower than the input voltage. Note that changing rSET will not noticeably affect the efficiency at max loads and also not at light loads for DCM but in the. Two different topologies are called buckboost converter.
Efficiency of Buck Converter Switching regulators are known as being highly efficient power sources. On the other hand if your voltage needs a boost goodbye buck and welcome to the boost converter which becomes the only game in town. The latest addition to this lineup is the LTC3532 a 300mA buck-boost converter which incorporates automatic Burst Mode operation adjustable switching frequency and integrated soft-start.
Not only are there many available on the market the designer has a myriad of trade-offs to consider. Its a popular choice where we need to convert higher voltage to a lower output voltage. This application note explains power loss factors and methods for calculating them.
Boost converter- The boost converter is used when a higher output voltage than the input voltage is required It contains ripple in converter which works with light load It is generally used in discontinuous mode. Fundamentals of Buck Converter Efficiency. If efficiency is not your priority heat is not a concern the current necessary is very small or V in is only slightly higher than V out an LDO can be usedBut if efficiency and performance are your utmost concern even if it is more complex and likely to be more expensive then a buck converter is the ideal choice.
This page compares Buck converter vs Boost converter and mentions difference between Buck converter and Boost converter. For a Boost the input cap RMS is very small so we can ignore that usually. In boost mode the output voltage is always greater than the input voltage because D is always greater than zero.
Similarly higher efficiency could be achieved in boost mode than in buck-boost mode due to fewer operating power devices and lower current stress. To remedy this the LM27313 standard asynchronous boost converter will be used to compare the calculated versus measured results of the efficiency estimations. Both of them can produce a range of output voltages ranging from much larger than the input voltage.
Where D is the duty cycle of Q2. I have tested a boost converter under different duty cycles. The LTC3532 is ideal for miniature disk-drive applications or any application that requires high efficiency.
Linear Technology offers a family of buck-boost converters capable of supplying from 200mA to 2A with excellent efficiency. Below 36V the buck-boost converter input current increases beyond the load current while the buck converter enters the 100 duty cycle dropout where the input current is limited to the load current. Shows a typical buck converter.
I know the voltage is related to the input voltage by V Vin1-D where D is the duty cycle. This converter operates in either the CCM or the DCM over the entire load current range thus providing a more direct comparison with the developed higher-order model.

Some Properties Of Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Download Scientific Diagram
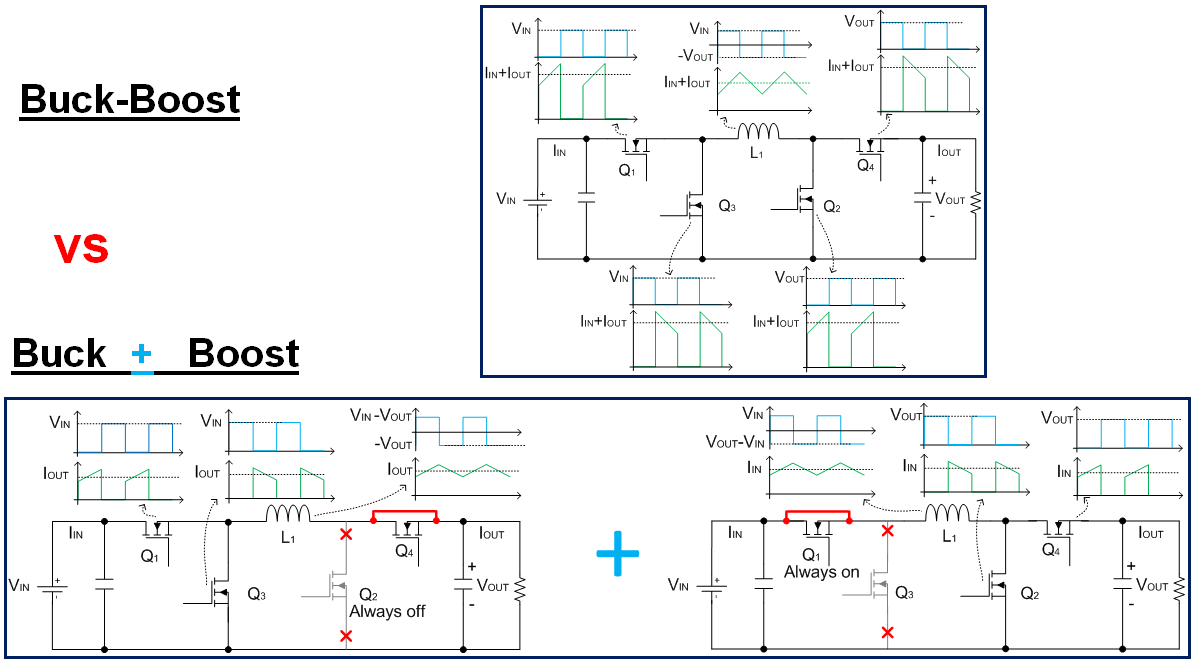
Do Not Operate A 4 Switch Buck Boost Converter In Buck Boost Mode Power Management Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

Some Properties Of Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Download Scientific Diagram

3a Output 96 Efficient Buck Boost Dc Dc Converter Sets The Standard For Power Density And Noise Performance Analog Devices
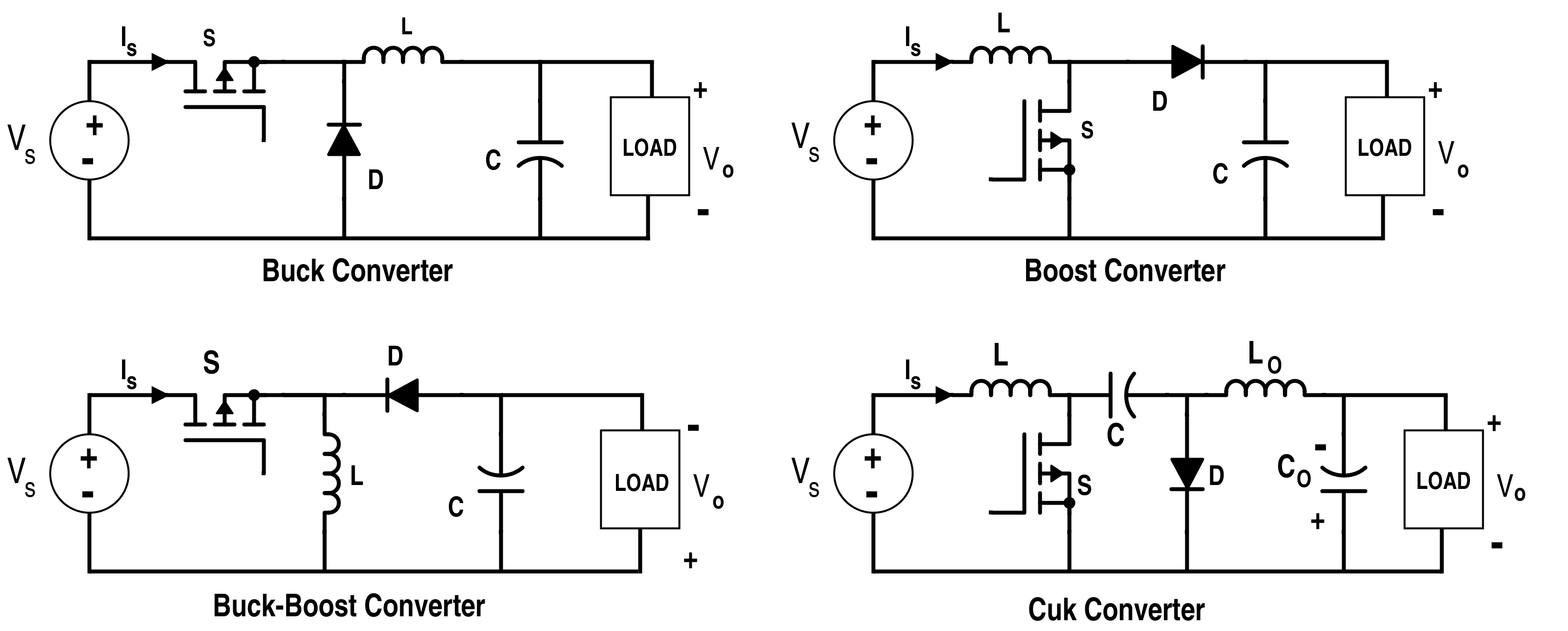
Analysis Of Four Dc Dc Converters In Equilibrium Technical Articles

A Topology Of H Bridge For The Buck Boost Converter And B Energy Download Scientific Diagram

Wide Vin And High Power Challenges With Buck Boost Converters Power Electronics
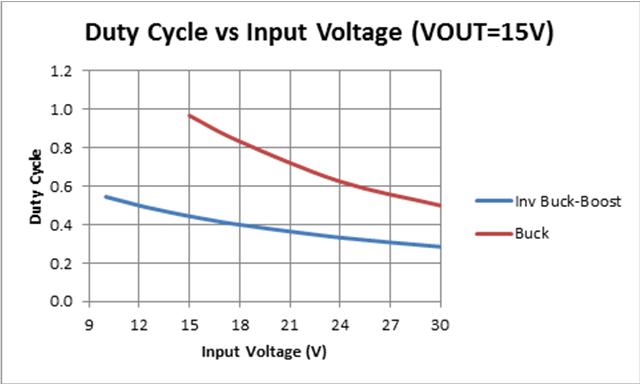
Should You Use Buck Or Inverting Topology For Fly Buck Power Management Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

An Introduction To Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Recom
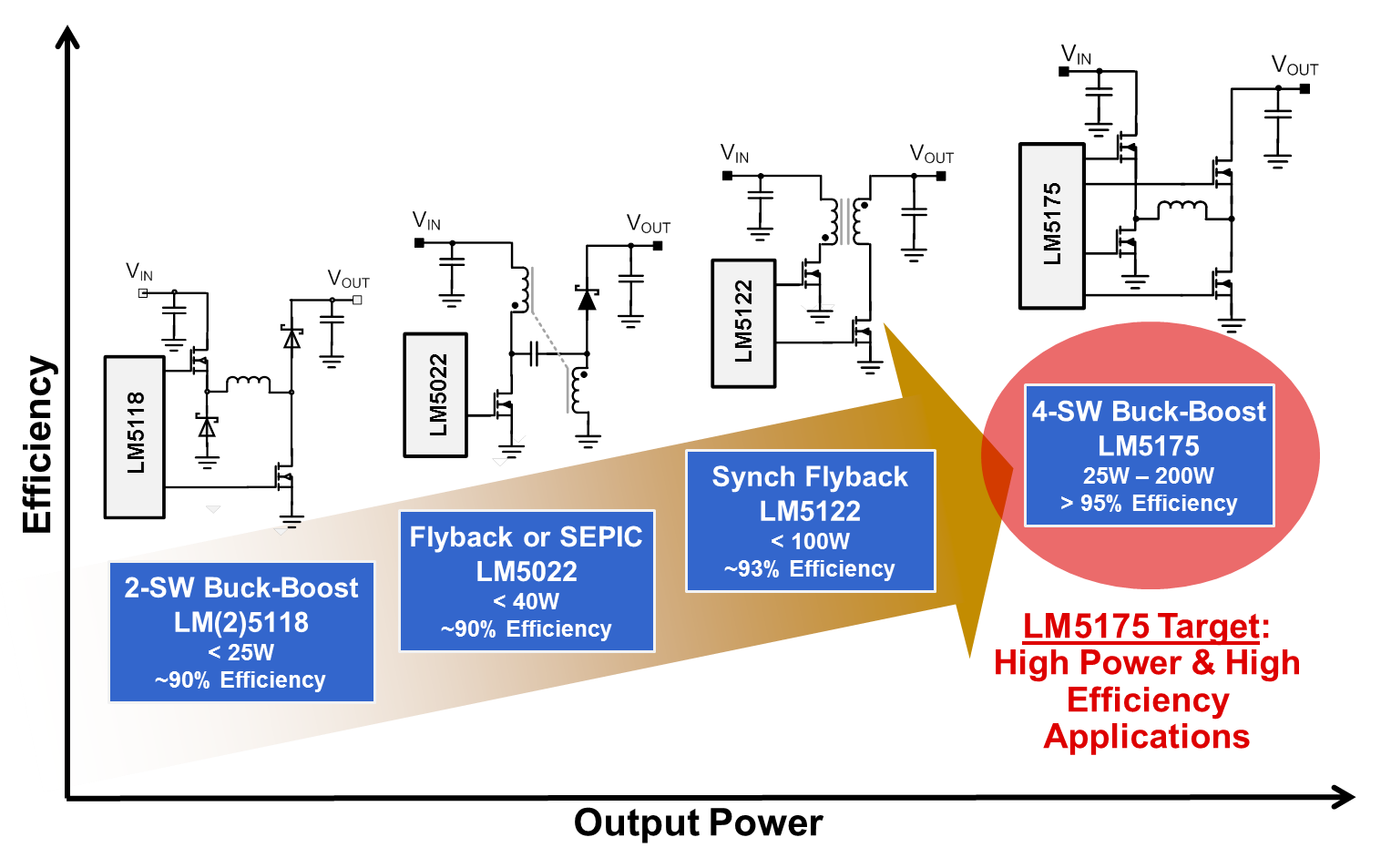
Four Switch Buck Boost Controller Delivers High Power And Efficiency Power Management Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

15v 2 5a Monolithic Buck Boost Dc Dc Converter With 95 Efficiency And Low Noise Operation Analog Devices

Schematic Diagram Of Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converter A Buck Download Scientific Diagram
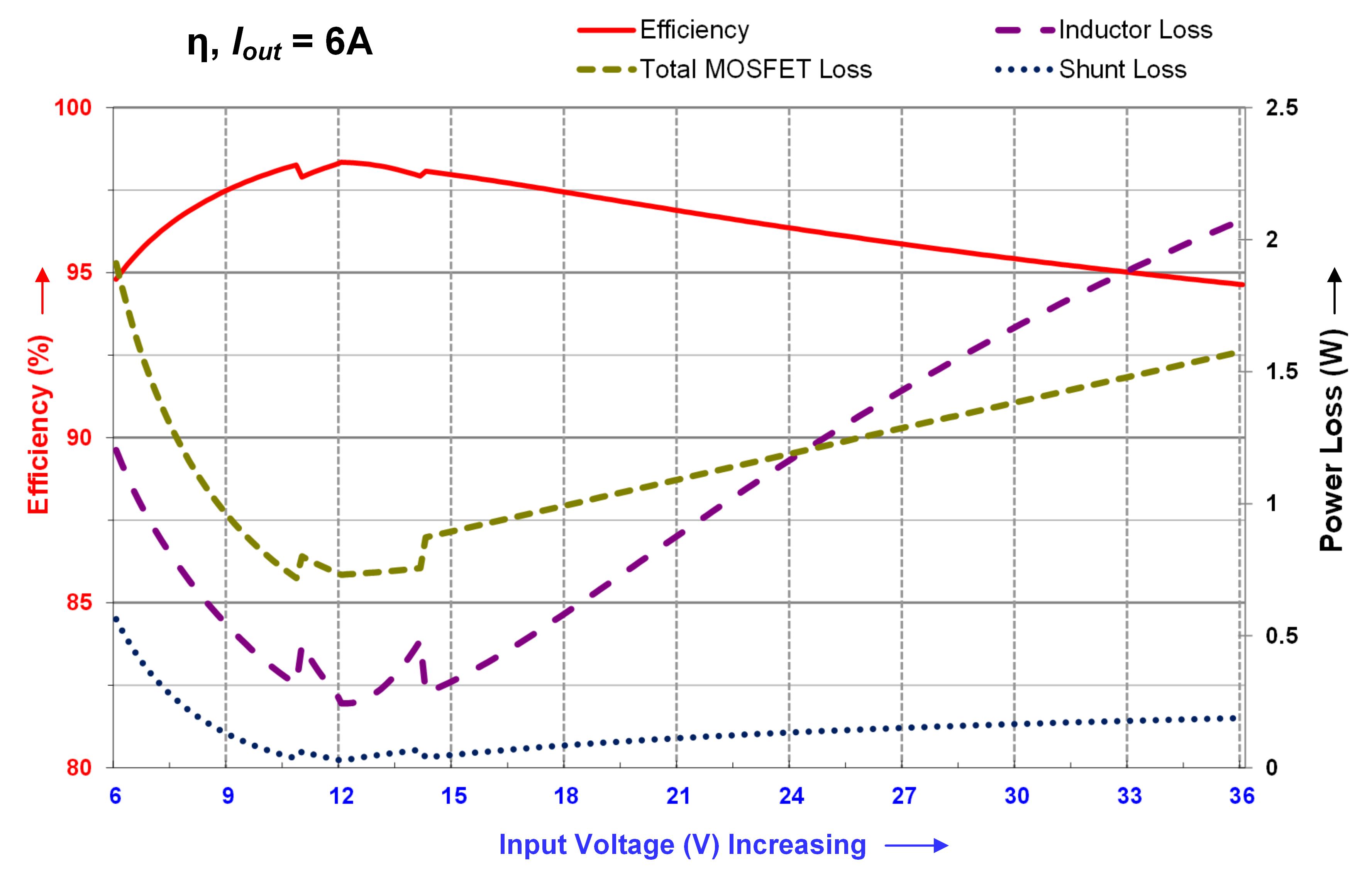
Increase Dc Dc Converter Efficiency Understanding Operating Modes And Power Losses Power Management Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

What S The Difference Between A Buck Convert And Boost Converter In Photovoltaics Sources Standalone Quora
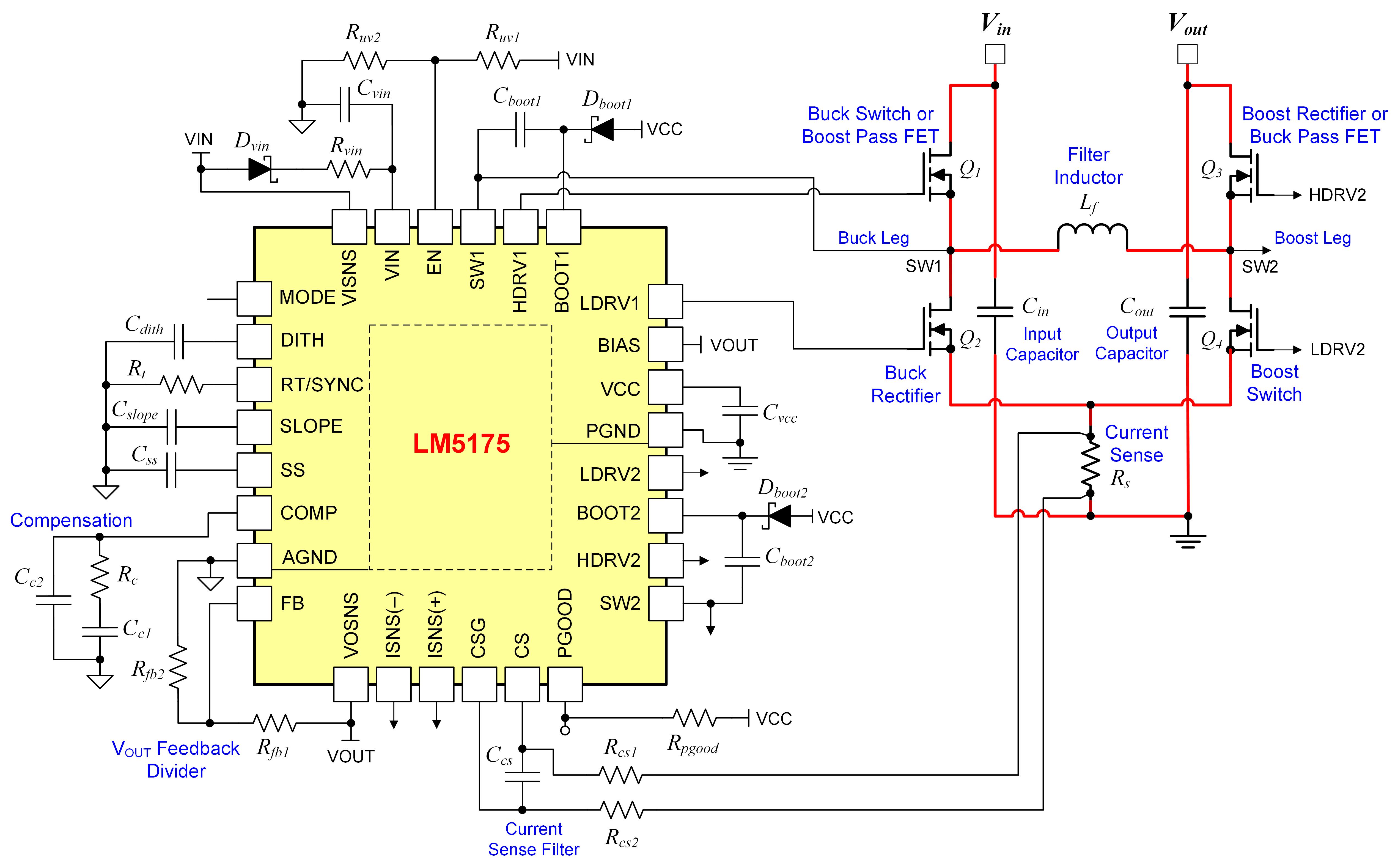
Increase Dc Dc Converter Efficiency Understanding Operating Modes And Power Losses Power Management Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

An Introduction To Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Recom

Buck Boost Vs Buck Converter It S About Battery Life In Portables Ee Times

Four Switch Buck Boost Converter In Buck Or Boost Mode Delivers The Highest Efficiency

Post a Comment for "Boost Vs Buck Converter Efficiency"